Difference between revisions of "Network Basics and Network Abstraction in Linux"
(→The ISO-OSI 7 Layer Model) |
(→The ISO-OSI 7 Layer Model) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The 7 Layer Model is used to describe networks. The IP Protocol has not been developed within ISO and thus only roughly fits into the mode. Still it is a good picture to have in you mind when you think about networks. |
The 7 Layer Model is used to describe networks. The IP Protocol has not been developed within ISO and thus only roughly fits into the mode. Still it is a good picture to have in you mind when you think about networks. |
||
| − | On Top you have your applications. Like e.g. a Web-Browser. |
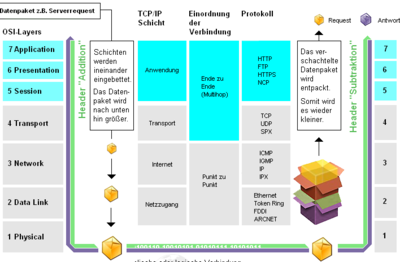
+ | On Top you have your applications. Like e.g. a Web-Browser. Below you need definitions on the details of how websites are encoded and transported via HTTP. And so on. And at the bottom we need specifications on |
| + | how data is transmitted at the wire (or wireless): E.g. cable definitions, voltage levels, frequency, etc.. |
||
| + | |||
| + | What we are looking at here is the Layer 2: That defines how data is encoded on a certain medium and in later units also layer3 (Routing - how packets are sent between networks). |
||
Revision as of 14:35, 24 March 2020
Motivation
Before you learn the tools and commands for using the network in Linux you need a basic understanding of how networks work and this unit tries to bring you up to speed quickly.
The ISO-OSI 7 Layer Model
The 7 Layer Model is used to describe networks. The IP Protocol has not been developed within ISO and thus only roughly fits into the mode. Still it is a good picture to have in you mind when you think about networks.
On Top you have your applications. Like e.g. a Web-Browser. Below you need definitions on the details of how websites are encoded and transported via HTTP. And so on. And at the bottom we need specifications on how data is transmitted at the wire (or wireless): E.g. cable definitions, voltage levels, frequency, etc..
What we are looking at here is the Layer 2: That defines how data is encoded on a certain medium and in later units also layer3 (Routing - how packets are sent between networks).